Technology
4 popular Apps for Laptop to Mobile File Transfer

5 Apps that you can use to transfer data wirelessly from your mobile device to your laptop.
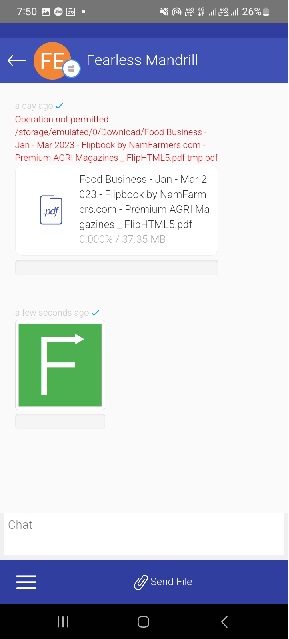
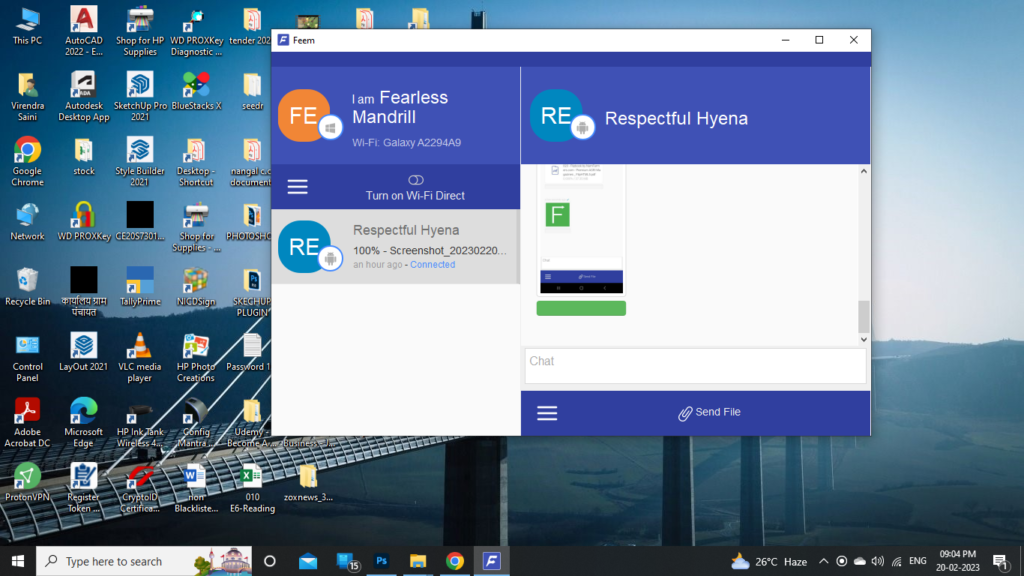
1. Feem
This is the application that should be in every system for someone who transfers large-size files like movies, software, or any other.
| Pros | Cons |
| No Limit | The free version works only for some folders to transfer. |
| Share file Offline | |
| Easy to connect and Use. | |
| No login is required like Airdroid |
Download link Click here
2. SHAREit
This app uses WiFi Direct to transfer files, photos, and videos between your mobile device and laptop. You can also transfer files to other devices that have SHAREit installed. Highly recommended.
| Pros | Cons |
| No Limit | |
| Share file Offline | |
| Easy to connect and Use. | |
| No login is required like Airdroid |
Download link Click here
3. Xender
This app also uses WiFi Direct to transfer files, photos, and videos between your mobile device and laptop. You can also transfer files to other devices that have Xender installed.
| Pros | Cons |
| No Limit | The free version works only for some folders to transfer. |
| Share file Offline | |
| Easy to connect and Use. | |
| No login is required like Airdroid |
Download link Click here
4. AirDroid
This app allows you to transfer files, photos, and videos wirelessly between your mobile device and laptop. You can also send and receive text messages, and manage your device from your laptop.


| Pros | Cons |
| Can be used without setup download by Airdroid web version login. | By Free version can transfer files of less than 30 MB only. |
| Can check mobile contact logs and call in laptop. | Have to Log in First on your Laptop and Mobile. |
Download link Click here
Note: These apps may require you to download the app on both your mobile device and laptop, and some may have limits on the amount of data you can transfer.