Uncategorized
All about Types of material for Wall Construction- Masonry Block

Masonry blocks are the main component of the wall. In 21 century, construction materials are changed instead of traditional materials. Here we will discuss all wall material mainly brick or block, which is the main component of a wall.
Many kinds of walls for a building are the Main wall, partition wall, retaining wall, boundary wall, parapet wall, etc.
Size, Shape, and strength vary for different types of walls. For the Partition wall, a minimum strength block is required which is safe for bearing self-load and the retaining wall block will be good under vertical and horizontal pressure strong.
Table of Contents
Further, we discuss the type of block used for different purposes available in the market.
Type of masonry block
- Based on the material of the block
- Based on shape of block
- Based on Manufacturing Type of block
Type of Masonry Block Based on Material of Block:
- Concrete block
- Fly Ash block
- AAC block
- Cinder block
1. Concrete Block
Masonry blocks made with concrete mortar only are concrete blocks. Concrete mortar consists of cement, sand, and aggregate. Concrete blocks are available in different sizes in the market. The strength of mortar decides block strength.
Read Also: Concrete blocks: Types, Tests Pros & manufacturing process
2. Fly Ash Block
Masonry blocks are made with concrete mortar which includes fly ash called fly ash Block. Fly ash is a waste product of coal thermal power plants. The use of fly ash in blocks makes an environment-friendly product and reduces the weight of the block.
3. AAC block
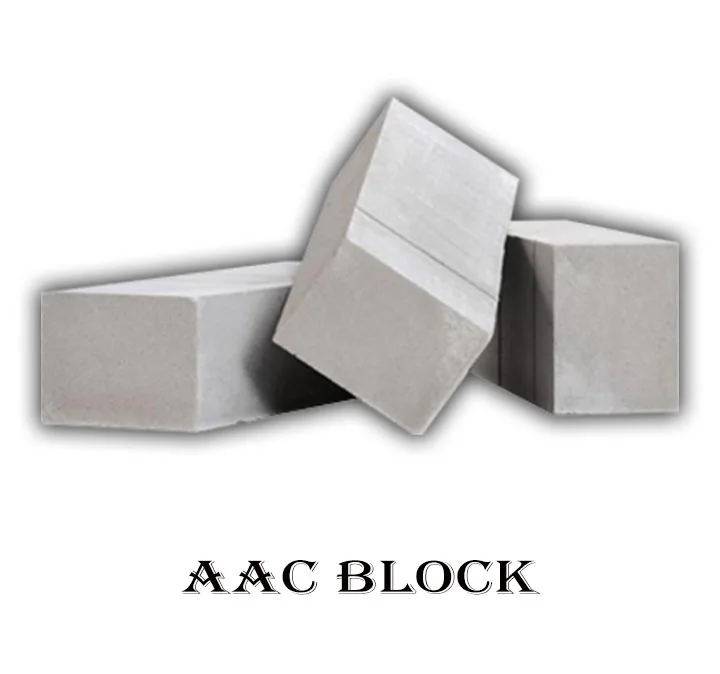

AAC (Autoclave aerated concrete) Block is a new kind of lightweight block used in multistory buildings. AAC blocks are not strong enough like clay bricks or concrete blocks, so used only in buildings where columns and beams are provided for load transfer, and blocks are used for partition walls only.
4. cinder block
Cinder blocks are similar to concrete blocks but are made from industrial waste materials such as coal cinders.
Type of Masonry Block Based on Shape of Block:
- Solid Block
- Hollow block
- Key/ interlock Block
- Beltis block
- Breeze block
1. Solid Block

A solid block is completely dense and has no open spaces inside it. Solid blocks are typically used in load-bearing walls or other structural applications where strength and durability are essential.
Solid blocks are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, including standard rectangular blocks, and corner blocks. Used in the construction of foundations, retaining walls, and structural walls.
2. Hollow Block

Hollow blocks are a type of masonry block that have one or more hollow cores or voids running through the middle. These voids can be either circular or rectangular in shape and are usually filled with a material such as concrete or insulation to improve the block’s strength and insulation properties.
Hollow blocks are commonly used in construction for non-load-bearing walls and partitions, as well as for decorative purposes.
3. Key/ interlock Block

Interlocking masonry blocks are a type of building block that is designed to fit together like puzzle pieces, without the need for mortar or other adhesives. These blocks have unique shapes that interlock with one another, creating a strong, stable, and secure connection. Interlocking masonry blocks are often used in construction for retaining walls, garden walls, and other landscaping projects, as well as for residential and commercial buildings.
One of the main advantages of using interlocking masonry blocks is their ease of installation. Because they do not require mortar, they can be quickly and easily installed by a trained professional or even a DIY enthusiast. This can save time and money during the construction process.
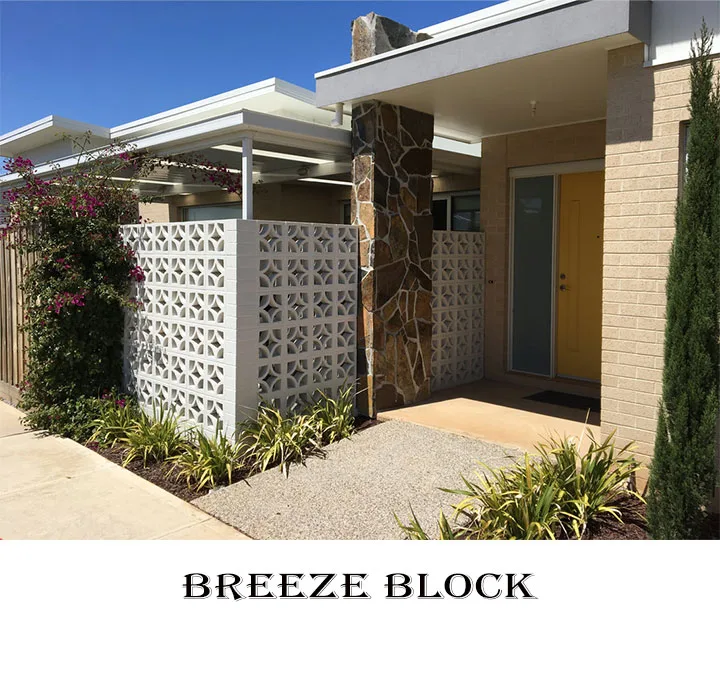
5. Breeze Block

Breeze blocks, also known as decorative blocks, have decorative patterns and are commonly used in architectural projects.
Read also: Needs of Many New City: Urban Development in India
Type of Masonry Block Based on Manufacturing of Block:
- Hydraulic pressed block
- Vibrated block
- Autoclave heated block
1. Hydraulic-pressed block
A type of masonry block that is manufactured using hydraulic pressure to compress and shape the block. These blocks are typically made from a mix of cement, sand, and other aggregates, which are mixed with water and then placed into a mold. The mold is then subjected to hydraulic pressure, which compacts the mixture and creates a dense, uniform block.
Advantages of using hydraulic pressed blocks
- Resistance to moisture and weathering.
- Uniform size and shape
- The dense, tightly compacted nature of these blocks makes them less susceptible to moisture intrusion and damage from freeze-thaw cycles.
- Fire-resistant, making them a good choice for construction projects where fire safety is a concern.
Disadvantages of using hydraulic pressed blocks
- Low insulation property
- Expensive due to the heavy machinery for manufacturing.
2. Vibrated block
During the manufacturing process, the concrete mixture is poured into a mold and then subjected to high-frequency vibration, which compacts the mixture and removes any air pockets. This creates a dense, uniform block that is stronger and more durable than other types of masonry blocks.
Advantages of using vibrated masonry blocks
- Good strength and durable
- Dense, well compacted
- less prone to cracking, chipping, or other forms of damage
- good insulation properties.
How to calculate the number of blocks?
The number of blocks depends on mainly two factors:
- Size of plot
- Size of the blocks
Assume A wall 8″ thick, 10′ long, and 9 feet high have to be constructed. And the size of block is 16″ X 8″ X 6″
- Leave the width of the block and thickness of the wall which is the same 8″.
- Area of wall = 10’*9′ = 90 square feet.
- Area of block = 16″*6″ = 96 square inch = 0.667 square feet.
- Number of blocks = area of wall/area of the block
- Number of blocks = 90/0.667 = 134.93
- Approx 135 blocks(16″x8″x6″) for 90 square feet of work required.